帖子
发帖
PostController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @ApiOperation(value = "新增")
@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()")
@PostMapping("/create")
public ApiResult<Post> create(@RequestBody PostDTO dto, Principal principal) {
User user = userService.getUserByUsername(principal.getName());
Post post = postService.create(dto, user);
return ApiResult.success(post);
}
|
@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()")注解表示需要登录才能访问。
此方法中两个参数表示,前端给后端发送数据的格式,以及当前登录用户的信息。
当调用此方法时会通过Spring的Principal对象获取当前登录用户的信息。再将用户信息和前端发送的数据进行处理。
PostServiceImpl.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| @Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Post create(PostDTO dto, User user) {
Post post1 = this.baseMapper.selectOne(new LambdaQueryWrapper<Post>().eq(Post::getTitle, wordFilter.replaceWords(dto.getTitle())));
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(post1)){
ApiAsserts.fail("标题重复,请重新编辑");
}
Post post = Post.builder()
.userId(user.getId())
.title(wordFilter.replaceWords(dto.getTitle()))
.content(EmojiParser.parseToAliases(wordFilter.replaceWords(dto.getContent())))
.createTime(new Date())
.build();
this.baseMapper.insert(post);
int newScore = user.getScore() + 1;
userMapper.updateById(user.setScore(newScore));
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(dto.getTags())){
List<Tag> tags = tagService.insertTags(dto.getTags());
postTagService.createPostTag(post.getId(),tags);
}
return post;
}
|
在此方法中,我们首先通过标题进行查询,如果查询到了相同的标题,则抛出异常。检查通过会通过lombok的@Builder注解进行封装,并将修改好的数据插入数据库。随之进行用户积分的增加与标签的保存。(在封装数据的时候会对帖子的标题以及内容进行敏感词过滤替换)
帖子详情
PostController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @ApiOperation(value = "详情")
@GetMapping()
public ApiResult<Map<String, Object>> view(@RequestParam("id") String id) {
Map<String, Object> map = postService.viewPost(id);
return ApiResult.success(map);
}
|
PostServiceImpl.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Override
public Map<String, Object> viewPost(String id) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
Post post = this.baseMapper.selectById(id);
Assert.notNull(post,"当前话题不存在,或已被作者删除");
post.setView(post.getView()+1);
this.baseMapper.updateById(post);
post.setContent(EmojiParser.parseToUnicode(post.getContent()));
map.put("post", post);
QueryWrapper<PostTag>wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.lambda().eq(PostTag::getTopicId, post.getId());
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (PostTag articleTag : postTagService.list(wrapper)){
set.add(articleTag.getTagId());
}
List<Tag> tags = tagService.listByIds(set);
map.put("tags", tags);
ProfileVO user = userService.getUserProfile(post.getUserId());
map.put("user", user);
return map;
}
|
查看帖子详情时,会首先判断数据库中是否存在这条数据。判断通过之后会将帖子的浏览量增加,并将帖子的内容转码。将转码后的帖子内容存进创建的map中。
封装好帖子信息之后,我们需要通过帖子id来查询当前帖子所关联的标签id。再通过这些标签id获得标签信息,并将结果封装进map。
第三步,我们需要通过帖子的作者id来查询作者的信息,并将结果封装进map。再将map封装进ApiResult返回。
评论
一级评论
CommentController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @ApiOperation(value = "新增评论")
@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()")
@PostMapping("/add_comment")
public ApiResult<Comment> add_comment(@RequestBody CommentDTO dto, Principal principal) {
if (dto.getContent() == null || "".equals(dto.getContent()) || "\n".equals(dto.getContent())) {
ApiAsserts.fail("评论内容不能为空");
}
User user = userService.getUserByUsername(principal.getName());
Comment comment = commentService.create(dto, user);
return ApiResult.success(comment);
}
|
在此方法中参数与上节发帖方法中的参数相同,不作过多解释。
在进入此方法时,会先检查评论内容是否为空,如果为空则抛出异常。 验证通过之后会调用getUserByUsername方法获取当前登录用户的信息,并将用户信息和前端发送的数据进行处理。
CommentServiceImpl.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Override
public Comment create(CommentDTO dto, User user) {
Comment comment = Comment.builder()
.userId(user.getId())
.content(wordFilter.replaceWords(dto.getContent()))
.topicId(dto.getTopic_id())
.createTime(new Date())
.build();
this.baseMapper.insert(comment);
messageService.createMessage(user.getId(),postService.getById(dto.getTopic_id()).getUserId() ,"评论了你的帖子:" + comment.getContent());
return comment;
}
|
这里首先对数据进行封装处理,并将封装结果插入数据库。然后调用messageService的createMessage方法,将当前评论的用户id和帖子的用户id作为参数传入,并将评论内容作为消息内容。
二级评论
CommentController.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @ApiOperation(value = "新增二级评论")
@PreAuthorize("isAuthenticated()")
@PostMapping("/add_child_comment")
public ApiResult<Comment> add_child_comment(@RequestBody ChildCommentDTO dto,Principal principal) {
if (dto.getChild_comment_content() == null || "".equals(dto.getChild_comment_content()) || "\n".equals(dto.getChild_comment_content())) {
ApiAsserts.fail("评论内容不能为空");
}
User user = userService.getUserByUsername(principal.getName());
Comment comment = commentService.create(dto, user);
return ApiResult.success(comment);
}
|
新增二级评论的方法逻辑其实是与上面的一级评论一样的,他们的不同只是二级评论在创建的时候会同时插入一级评论的id作为roo_id。
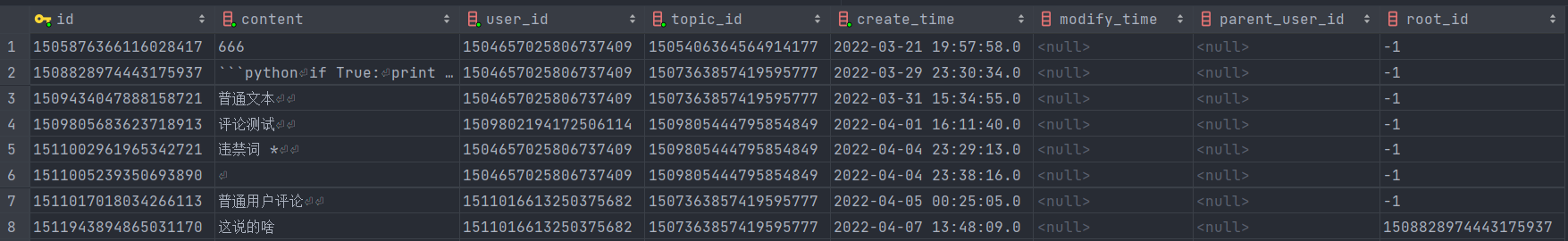
从这个表中其实可以看到,一级评论的root_id属性都是空的,而二级评论的root_id属性都是一级评论的id。下面来介绍一下二级评论的具体实现。
CommentServiceImpl.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Override
public Comment create(ChildCommentDTO dto, User user) {
Comment comment = Comment.builder()
.userId(user.getId())
.content(wordFilter.replaceWords(dto.getChild_comment_content()))
.topicId(this.getById(dto.getContent_parent_id()).getTopicId())
.rootId(dto.getContent_parent_id())
.createTime(new Date())
.build();
this.baseMapper.insert(comment);
return comment;
}
|
这里首先对数据进行封装处理,并将封装结果插入数据库。然后调用getById方法获取父评论的信息,并将父评论的topicId属性作为该二级评论的root_Id属性。


